Burtom ‣ Technologies ‣ Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT)
Language: 🇬🇧 English | 🇹🇷 Türkçe
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) Overview

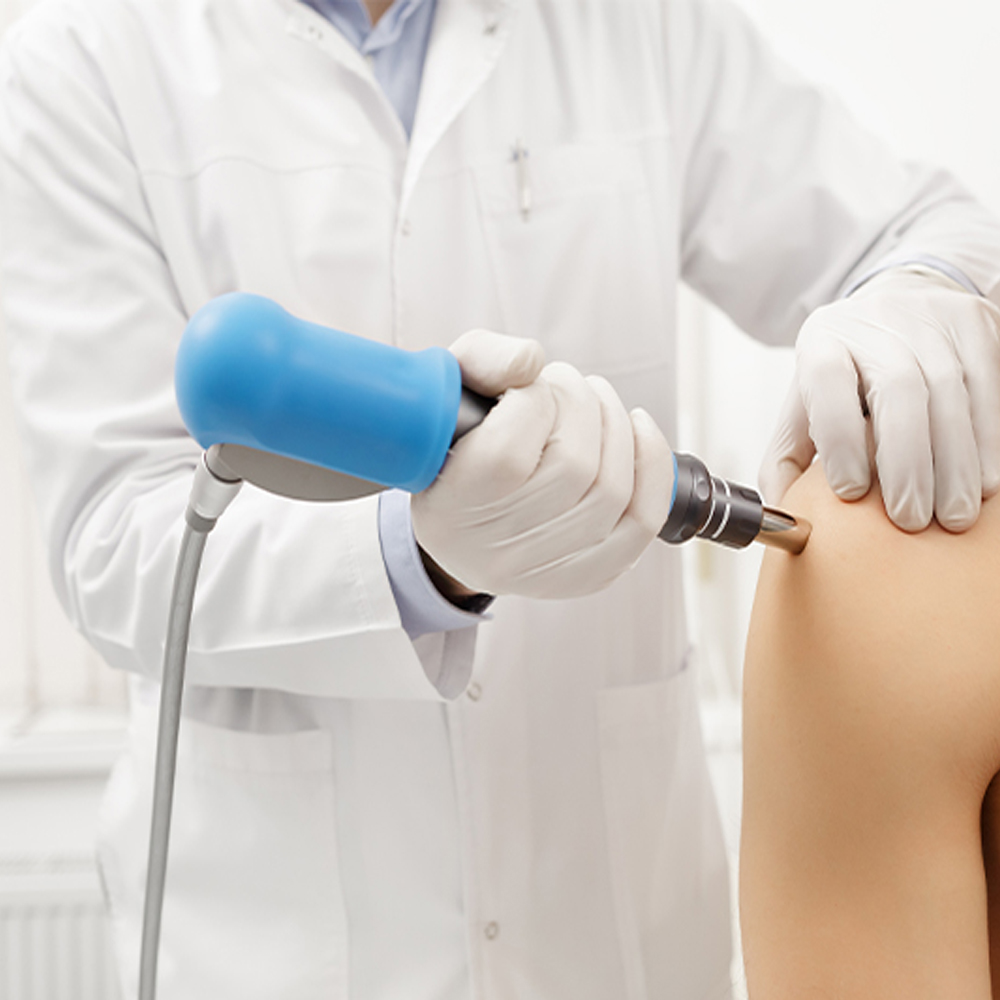
 Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) is a non-invasive medical procedure that utilizes shockwaves to treat various musculoskeletal conditions. During the procedure, shockwaves are generated outside the body and then directed towards the affected area. These shockwaves deliver mechanical energy to the tissues, stimulating the body’s natural healing response. ESWT has been used to effectively manage conditions such as plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendinopathy, calcific tendinitis, and tennis elbow.
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) is a non-invasive medical procedure that utilizes shockwaves to treat various musculoskeletal conditions. During the procedure, shockwaves are generated outside the body and then directed towards the affected area. These shockwaves deliver mechanical energy to the tissues, stimulating the body’s natural healing response. ESWT has been used to effectively manage conditions such as plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendinopathy, calcific tendinitis, and tennis elbow.
One of the key advantages of ESWT is its ability to promote tissue regeneration and repair without the need for surgery or invasive procedures. The shockwaves delivered during ESWT help to increase blood flow to the affected area, which can accelerate the healing process. Additionally, ESWT has been shown to have analgesic effects, reducing pain associated with musculoskeletal disorders. This makes it a valuable treatment option for individuals seeking non-invasive pain relief and improved functionality.
ESWT is typically performed as an outpatient procedure and does not require anesthesia, making it a convenient option for many patients. The treatment is usually administered in a series of sessions, with each session lasting approximately 15 to 20 minutes. While some patients may experience mild discomfort during the procedure, ESWT is generally well-tolerated and associated with minimal side effects. Overall, ESWT offers a promising alternative for individuals seeking effective, non-invasive treatment options for various musculoskeletal conditions.
The Basic Principle and Purpose of ESWT

The fundamental principle of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) lies in its application of shockwaves to targeted areas of the body, with the primary purpose of stimulating the body’s natural healing response. ESWT utilizes high-energy acoustic waves to promote tissue regeneration, reduce pain, and improve mobility in various musculoskeletal conditions.
Mechanism and Effects of Shock Wave Generation:
Shock waves are generated using specialized devices that deliver high-energy acoustic pulses to targeted areas of the body. These shock waves are characterized by their rapid pressure changes and high amplitude, which create a mechanical force capable of penetrating deep into tissues.
The mechanism behind shock wave generation involves the conversion of kinetic energy into acoustic energy. This is typically achieved using an electromagnetic or piezoelectric mechanism within the shock wave generator. When activated, these mechanisms produce a rapid and focused pressure wave that propagates through the tissues, inducing various physiological responses.
The effects of shock wave generation on biological tissues are diverse and include mechanical, biochemical, and cellular responses. At the cellular level, shock waves stimulate the release of growth factors, enhance cellular metabolism, and promote tissue regeneration. They also disrupt tissue structures, such as calcifications and scar tissue, leading to their breakdown and eventual elimination from the body.
Overall, shock wave generation is a versatile therapeutic modality that can produce a range of effects beneficial for tissue healing, pain relief, and functional improvement in various musculoskeletal and orthopedic conditions.
Applications and Importance of ESWT:
ESWT, or Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy, has a wide range of applications across various medical fields due to its effectiveness in promoting tissue healing and pain relief. One of the primary applications of ESWT is in the treatment of musculoskeletal conditions, including tendon and ligament injuries, plantar fasciitis, and calcific tendonitis. By delivering focused shock waves to the affected area, ESWT stimulates tissue regeneration, reduces inflammation, and promotes healing.
In addition to musculoskeletal disorders, ESWT is also used in the management of orthopedic conditions such as non-union fractures and avascular necrosis. The shock waves help to stimulate bone growth and improve blood flow to the affected area, facilitating the healing process.
Furthermore, ESWT has shown promising results in the treatment of certain chronic pain conditions, such as chronic plantar fasciitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome. By targeting the underlying pathology and promoting tissue repair, ESWT can provide long-lasting pain relief and improve overall quality of life for patients.
Overall, the importance of ESWT lies in its ability to offer non-invasive and effective treatment options for a wide range of medical conditions. By harnessing the power of shock waves, ESWT provides patients with a safe and efficient alternative to traditional therapies, allowing for faster recovery and improved outcomes.
Management of Musculoskeletal Disorders:
Musculoskeletal disorders encompass a broad range of conditions affecting the muscles, bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, and nerves, often resulting in pain, inflammation, and functional limitations. The management of musculoskeletal disorders involves a multidisciplinary approach aimed at alleviating symptoms, restoring function, and improving the overall quality of life for affected individuals.
One essential aspect of managing musculoskeletal disorders is the use of advanced therapeutic modalities such as Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT). ESWT employs high-energy shock waves to target and stimulate damaged tissues, promoting healing and reducing pain without the need for invasive procedures.
ESWT technology relies on the generation of shock waves, which are acoustic waves characterized by rapid pressure changes. These shock waves are generated outside the body using a specialized device and then focused on the affected area using an applicator or probe.
The basic components of an ESWT device typically include a control unit, a shock wave generator, and an applicator. The control unit allows the operator to adjust parameters such as shock wave intensity, frequency, and treatment duration based on the patient’s specific condition and treatment goals.
The shock wave generator is responsible for producing the high-energy shock waves used in therapy. These shock waves are generated by rapidly accelerating a projectile within a pressurized cylinder, resulting in the creation of acoustic waves that propagate through the body tissues.
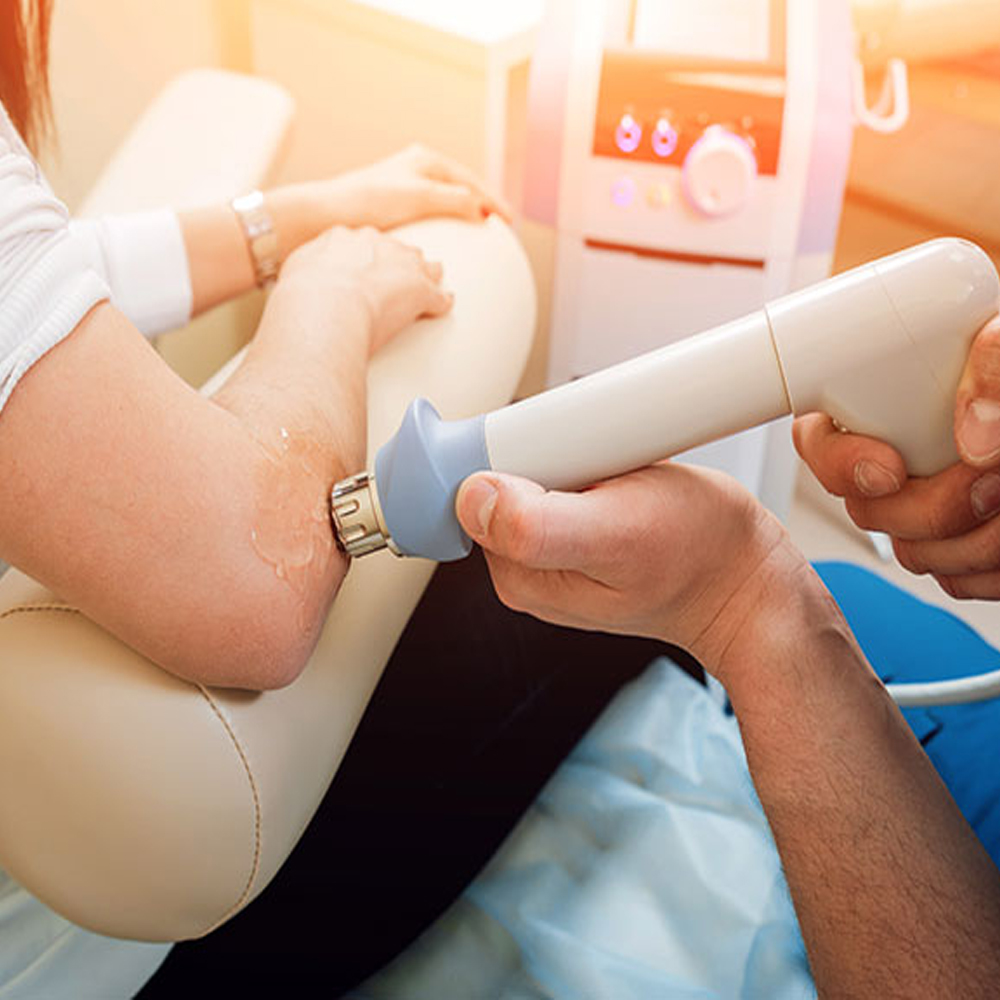
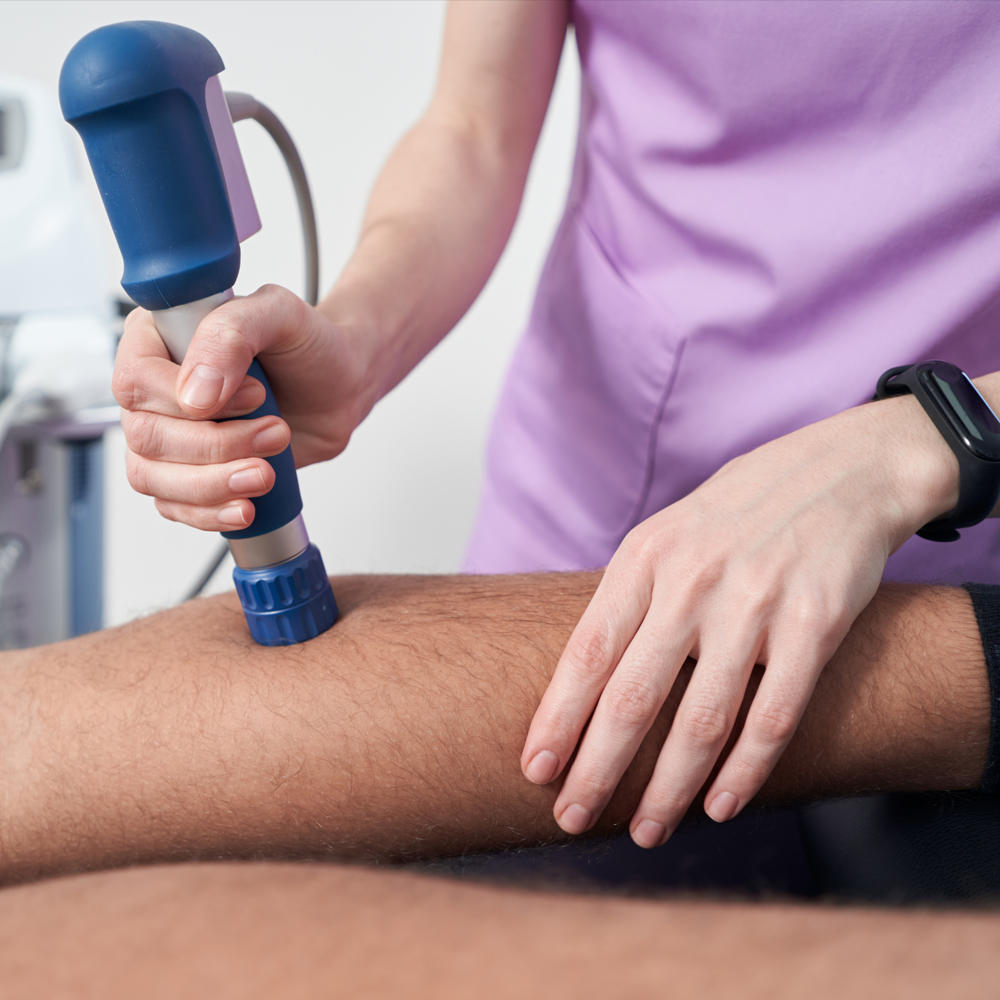
The applicator is the interface between the shock wave generator and the patient’s body. It consists of a coupling medium, such as gel or water, to transmit the shock waves efficiently to the target tissue. The applicator also features a focusing mechanism to concentrate the shock waves on the desired treatment area, ensuring maximum therapeutic effect.
During an ESWT session, the patient typically lies in a comfortable position, and the applicator is placed directly over the affected area. The shock waves are then delivered in controlled pulses, penetrating deep into the tissues to stimulate healing processes and alleviate pain.
Overall, ESWT represents a valuable therapeutic option in the management of musculoskeletal disorders, offering a non-invasive, safe, and effective approach to promoting tissue healing and restoring function in patients with various orthopedic and sports-related injuries.
Generation and Focusing of Shock Waves:
The generation and focusing of shock waves are fundamental aspects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT), a non-invasive treatment modality used for various musculoskeletal conditions. Shock waves are acoustic waves characterized by rapid pressure changes that propagate through tissues and can induce biological effects beneficial for tissue healing and pain relief.
In ESWT, shock waves are generated using a specialized device known as a shock wave generator. This device typically consists of a cylindrical chamber filled with a pressurized gas medium, such as air or helium, and a projectile mechanism. When triggered, the projectile is rapidly accelerated within the chamber, generating a high-energy acoustic wave that propagates outward from the source.
To focus the shock waves on the target tissue, ESWT devices utilize an acoustic lens or reflector system. These focusing mechanisms are designed to concentrate the shock waves into a narrow beam, allowing precise targeting of the affected area while minimizing dispersion and loss of energy. This focused delivery enhances the therapeutic effectiveness of ESWT and reduces the risk of damage to surrounding tissues.
Clinical Applications of ESWT:
ESWT has a wide range of clinical applications across various medical specialties, particularly in the fields of orthopedics, sports medicine, and rehabilitation. Some of the common clinical applications of ESWT include:
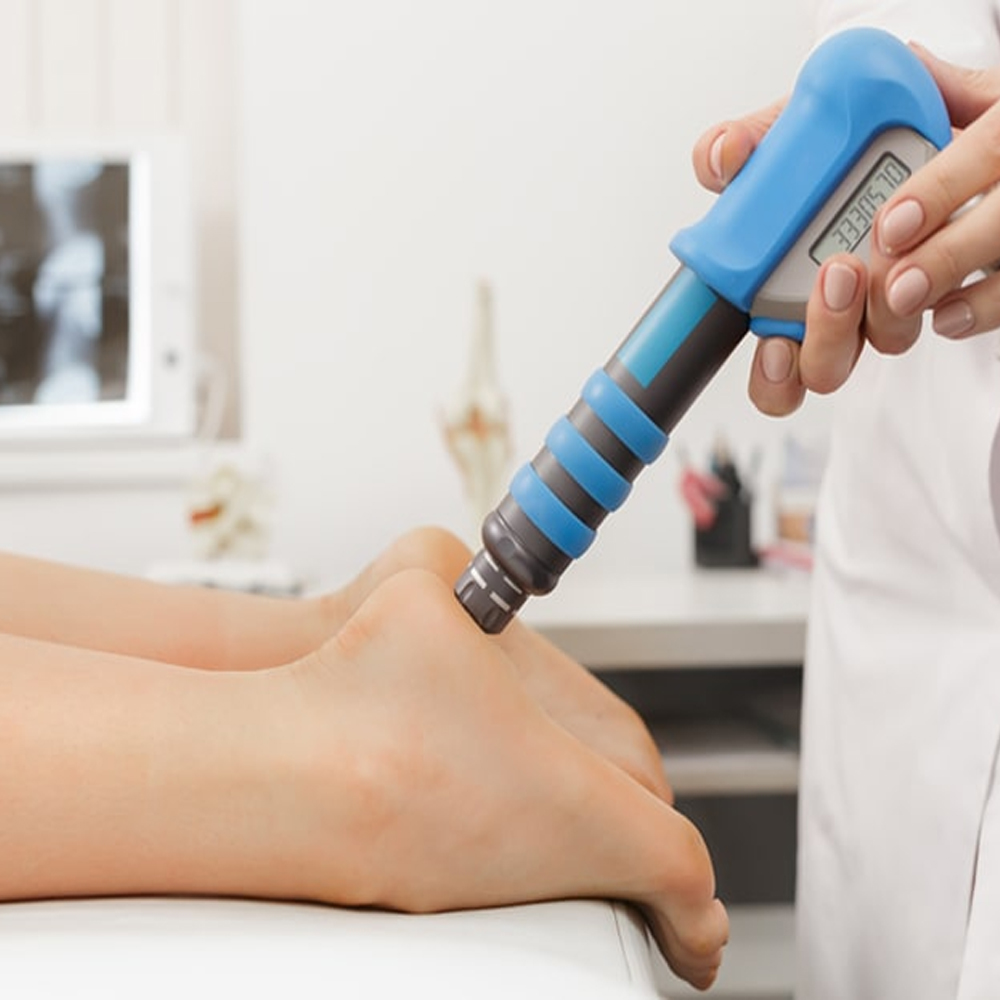
Tendon Disorders: ESWT is frequently used to treat tendon disorders such as plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendinopathy, and patellar tendinopathy. Shock waves can stimulate tissue regeneration, improve blood flow, and reduce inflammation in damaged tendons, leading to pain relief and improved functional outcomes.
Musculoskeletal Pain: ESWT is effective in managing musculoskeletal pain conditions, including chronic back pain, shoulder pain, and tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis). Shock waves can modulate pain signaling pathways, promote tissue healing, and induce analgesic effects, providing long-lasting pain relief for patients.
Bone Healing: ESWT has been utilized to enhance bone healing in conditions such as non-union fractures and delayed union fractures. Shock waves stimulate osteogenesis (bone formation) and angiogenesis (blood vessel formation), accelerating the healing process and improving fracture union rates.
Soft Tissue Injuries: ESWT can aid in the rehabilitation of soft tissue injuries such as muscle strains, ligament sprains, and contusions. Shock waves promote tissue regeneration, reduce scar formation, and improve tissue elasticity, facilitating faster recovery and return to activity.
Chronic Conditions: ESWT is also beneficial for chronic musculoskeletal conditions such as osteoarthritis and fibromyalgia. Shock waves can modulate inflammatory processes, improve joint function, and alleviate pain associated with chronic degenerative conditions, enhancing patients’ quality of life.
Overall, ESWT is a versatile and effective treatment modality with broad clinical applications, offering non-invasive pain relief and tissue regeneration for a wide range of musculoskeletal disorders.
Treatment of Tendon and Ligament Injuries:
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) is widely used for the treatment of tendon and ligament injuries due to its ability to stimulate tissue regeneration and promote healing. Tendon and ligament injuries often result from overuse, repetitive stress, or trauma, leading to pain, inflammation, and reduced function. ESWT delivers focused shock waves to the affected area, initiating biological responses that enhance blood flow, stimulate cellular activity, and promote tissue repair. This process helps to accelerate the healing of tendon and ligament injuries, improve tissue strength and flexibility, and alleviate symptoms such as pain and stiffness.
Rehabilitation of Calcifications and Muscle Strains:
ESWT is also utilized in the rehabilitation of calcifications and muscle strains. Calcifications, or calcium deposits, can develop within soft tissues such as tendons due to injury or degenerative conditions like tendinopathy. These deposits can cause pain and restrict movement. ESWT targets calcifications with focused shock waves, disrupting the deposits and promoting their resorption by the body’s natural processes. This leads to the gradual breakdown and elimination of calcifications, relieving pain and restoring function.
Muscle strains, which involve the stretching or tearing of muscle fibers, are common injuries that can occur during physical activity or sports participation. ESWT can aid in the rehabilitation of muscle strains by promoting tissue healing, reducing inflammation, and improving muscle function. Shock waves stimulate the repair processes within the injured muscle, leading to the formation of new muscle tissue and improved strength and flexibility. Additionally, ESWT can help prevent the formation of scar tissue, allowing for more efficient healing and rehabilitation of muscle strains.
Overall, ESWT is an effective treatment option for tendon and ligament injuries, as well as calcifications and muscle strains. Its non-invasive nature, minimal side effects, and ability to promote tissue regeneration make it a valuable tool in musculoskeletal rehabilitation, helping patients recover from a variety of soft tissue injuries and conditions.
Advantages and Benefits of ESWT:
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) offers several advantages and benefits as a non-invasive treatment modality for various musculoskeletal conditions:
Non-Invasive: ESWT is a non-surgical and non-invasive treatment option, making it suitable for patients who wish to avoid surgery or have contraindications for surgical interventions.
Pain Relief: ESWT has analgesic effects and can provide effective pain relief for chronic musculoskeletal conditions such as plantar fasciitis, tendinopathies, and myofascial pain syndromes.
Tissue Regeneration: Shock waves stimulate tissue regeneration by promoting angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels) and enhancing the production of growth factors, which can facilitate the healing of tendons, ligaments, and bones.
Fast Recovery: ESWT is associated with faster recovery times compared to traditional treatment modalities. Patients typically experience improved symptoms and functional outcomes within a few weeks after treatment.
Outpatient Procedure: ESWT is performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home immediately after the procedure and resume their daily activities with minimal downtime.
Minimal Side Effects: ESWT is generally well-tolerated with minimal side effects. Common side effects may include mild discomfort or bruising at the treatment site, which usually resolves quickly.
Versatility: ESWT can be used to treat a wide range of musculoskeletal conditions, including tendinopathies, ligament injuries, osteoarthritis, and bone fractures, making it a versatile treatment option for orthopedic and sports medicine practices.
Cost-Effective: Compared to surgical interventions or prolonged medication use, ESWT can be a cost-effective treatment option in the long term, especially considering the potential reduction in healthcare expenses associated with chronic pain management.
Fast Rehabilitation and Healing Process:
ESWT has been shown to accelerate the rehabilitation and healing process for various musculoskeletal conditions:
Enhanced Tissue Healing: Shock waves stimulate cellular metabolism and increase blood flow to the affected area, promoting tissue regeneration and accelerating the healing process.
Reduced Inflammation: ESWT modulates inflammatory pathways and reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, leading to a faster resolution of inflammation and pain.
Improved Functional Outcomes: Patients undergoing ESWT often experience improved range of motion, strength, and functional outcomes, allowing them to return to their normal activities more quickly.
Reduced Rehabilitation Time: ESWT can shorten the rehabilitation period for musculoskeletal injuries, enabling patients to resume their daily activities and sports participation sooner than with conventional treatments.
Risks and Side Effects of ESWT:
While ESWT is generally safe and well-tolerated, there are some potential risks and side effects associated with the treatment:
Discomfort: Some patients may experience mild discomfort or pain during the ESWT procedure, especially if higher energy levels are used. However, this discomfort is usually temporary and can be managed with local anesthesia or analgesics.
Bruising and Swelling: Temporary bruising, swelling, or redness at the treatment site are common side effects of ESWT. These side effects typically resolve within a few days after the procedure.
Rare Complications: Although rare, serious complications such as skin burns, hematomas, or nerve damage may occur with ESWT, particularly if the treatment is administered incorrectly or at excessive energy levels.
Contraindications: ESWT may not be suitable for patients with certain medical conditions or risk factors, such as pregnancy, bleeding disorders, pacemakers, or active infections. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider is essential to determine the suitability of ESWT for individual patients.
Overall, the benefits of ESWT often outweigh the potential risks, especially when performed by experienced healthcare professionals in appropriate clinical settings. Patients should discuss their medical history and any concerns with their healthcare provider before undergoing ESWT treatment.
Potential Complications and Precautions:
Skin Burns: ESWT may cause skin burns if the shock waves are applied with excessive energy or incorrect settings. Proper calibration and monitoring of energy levels are essential to minimize this risk.
Hematomas: In rare cases, ESWT can lead to the formation of hematomas (localized blood clots) at the treatment site. Careful application of shock waves and monitoring for signs of excessive bleeding can help prevent this complication.
Nerve Damage: Improper application of ESWT, particularly near nerve-rich areas, may result in nerve damage. Precise targeting of shock waves and avoiding sensitive structures can reduce the risk of nerve injury.
Contraindications: Patients with certain medical conditions or risk factors, such as pregnancy, bleeding disorders, pacemakers, or active infections, may not be suitable candidates for ESWT. A thorough assessment of patient history and contraindications is crucial before proceeding with treatment.
Considerations During Treatment:
Energy Levels: ESWT devices allow for adjustable energy levels to be applied during treatment. Healthcare providers should carefully adjust energy settings based on the patient’s condition and response to therapy to optimize treatment outcomes while minimizing the risk of complications.
Shock Wave Delivery: Proper positioning and alignment of the ESWT applicator are essential to ensure accurate delivery of shock waves to the target area. Healthcare providers should carefully maneuver the device to effectively treat the intended pathology.
Patient Feedback: Continuous communication with the patient during treatment is important to monitor their comfort level and address any concerns or discomfort promptly. Patients should feel comfortable expressing any discomfort or pain experienced during the procedure.
Patient Experience and Comfort During ESWT Use:
Pain Management: ESWT may cause mild discomfort or pain during the procedure, especially at higher energy levels. Healthcare providers can employ various pain management techniques, such as local anesthesia or analgesics, to enhance patient comfort during treatment.
Communication: Healthcare providers should maintain open communication with patients throughout the ESWT session, explaining the procedure, addressing any questions or concerns, and ensuring patient cooperation and comfort.
Positioning and Support: Patients should be comfortably positioned during ESWT treatment to minimize movement and enhance treatment efficacy. Supportive cushions or positioning aids may be used to optimize patient comfort and stability.
Monitoring Vital Signs: Healthcare providers should monitor vital signs, such as heart rate and blood pressure, during ESWT treatment to ensure patient safety and well-being. Prompt action should be taken in case of any adverse reactions or complications.
Overall, ensuring patient safety, comfort, and effective treatment delivery are paramount considerations during ESWT use. Healthcare providers should adhere to established protocols, closely monitor patients during treatment, and address any complications or concerns promptly to optimize treatment outcomes.
Patient Impressions and Comfort During Treatment:
During extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), ensuring patient comfort and managing expectations play crucial roles in enhancing the treatment experience. Healthcare providers should strive to create a supportive and reassuring environment for patients undergoing ESWT. Here are some key aspects related to patient impressions and comfort during treatment:
Communication: Clear communication is essential to address any concerns or questions that patients may have regarding the ESWT procedure. Healthcare providers should explain the treatment process, potential sensations or discomfort, and expected outcomes to manage patient expectations effectively.
Pain Management: While ESWT is generally well-tolerated, patients may experience mild discomfort or sensations of pressure during the procedure. Healthcare providers can offer strategies to manage pain or discomfort, such as adjusting energy levels, using topical anesthesia, or providing relaxation techniques.
Patient Feedback: Encouraging open communication and feedback from patients throughout the treatment session is important. Healthcare providers should regularly check in with patients to assess their comfort level, address any discomfort promptly, and ensure that they feel supported throughout the procedure.
Comfortable Environment: Creating a comfortable treatment environment can contribute to a positive patient experience. This may include providing amenities such as comfortable seating, adjusting room temperature, and ensuring privacy during the procedure.
Post-Treatment Recovery and Patient Satisfaction:
After completing the ESWT session, patients’ post-treatment recovery and overall satisfaction are essential considerations. Here are some factors related to post-treatment recovery and patient satisfaction:
Recovery Guidelines: Providing clear instructions for post-treatment care and recovery is crucial to support optimal healing and outcomes. Healthcare providers should educate patients on any activity restrictions, self-care measures, and potential side effects to watch for after ESWT.
Follow-Up Care: Scheduling follow-up appointments allows healthcare providers to monitor patients’ progress, address any concerns or complications, and make adjustments to the treatment plan if needed. Follow-up visits also provide an opportunity to evaluate treatment outcomes and discuss further steps in the patient’s care journey.
Patient Education: Offering comprehensive patient education materials or resources about ESWT, including its mechanism of action, expected outcomes, and potential side effects, can empower patients to actively participate in their recovery process and make informed decisions about their care.
Assessing Patient Satisfaction: Regularly assessing patient satisfaction through surveys, feedback forms, or direct discussions allows healthcare providers to gauge the effectiveness of ESWT and identify areas for improvement in patient care and service delivery.
By prioritizing patient comfort, providing thorough post-treatment care, and actively seeking patient feedback, healthcare providers can contribute to positive treatment experiences, enhance patient satisfaction, and optimize outcomes following ESWT.
Patient Rights and Considerations Regarding ESWT:
Patients undergoing extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) are entitled to certain rights and considerations to ensure their safety, privacy, and overall well-being throughout the treatment process. Here are some key aspects related to patient rights and considerations regarding ESWT:
Informed Consent: Prior to undergoing ESWT, patients have the right to receive clear and comprehensive information about the procedure, including its purpose, potential risks and benefits, alternative treatment options, and expected outcomes. Patients must provide informed consent voluntarily, understanding the nature of the treatment and any associated implications.
Right to Privacy: Patients have the right to privacy and confidentiality regarding their medical information and treatment. Healthcare providers should maintain strict confidentiality of patient records and information, adhering to relevant privacy laws and regulations.
Respect for Dignity and Autonomy: Patients have the right to be treated with dignity, respect, and autonomy throughout the ESWT process. Healthcare providers should involve patients in treatment decisions, consider their preferences and concerns, and respect their autonomy in choosing or declining treatment options.
Access to Information: Patients have the right to access relevant information about their ESWT treatment, including details about the procedure, potential risks, expected outcomes, and post-treatment care instructions. Healthcare providers should address patients’ questions and concerns transparently, providing information in a clear and understandable manner.
Privacy and Data Protection:
Ensuring patient privacy and data protection is essential in ESWT practice to maintain confidentiality and safeguard sensitive medical information. Here are some considerations related to privacy and data protection:
Confidentiality Measures: Healthcare providers should implement robust confidentiality measures to protect patient information, including secure storage of medical records, restricted access to patient data, and encryption of electronic communication systems.
Compliance with Privacy Laws: Healthcare facilities must adhere to relevant privacy laws and regulations governing the collection, use, and disclosure of patient information, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States or the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union.
Patient Consent for Data Sharing: Healthcare providers should obtain explicit consent from patients before sharing their medical information or treatment records with third parties, ensuring transparency and respecting patient autonomy in data sharing decisions.
Data Security Measures: Implementing robust data security measures, such as encryption, firewalls, and regular security audits, helps safeguard patient information from unauthorized access, data breaches, or cyber threats.
Patient Rights and Preferences During Treatment:
During ESWT treatment sessions, patients have the right to express their preferences, voice any concerns, and actively participate in decisions affecting their care. Here are some considerations related to patient rights and preferences during treatment:
Communication and Collaboration: Healthcare providers should foster open communication and collaboration with patients during ESWT sessions, encouraging them to express their preferences, concerns, and feedback regarding the treatment process.
Comfort and Well-being: Patients have the right to receive compassionate and supportive care during ESWT sessions, including measures to enhance their comfort, minimize discomfort, and address any physical or emotional needs that may arise.
Respect for Cultural and Personal Beliefs: Healthcare providers should respect patients’ cultural and personal beliefs, preferences, and values during ESWT treatment, adapting care approaches to accommodate individual cultural backgrounds and preferences.
Patient-Centered Care: Adopting a patient-centered approach involves tailoring ESWT treatment to meet the unique needs, preferences, and goals of each patient, promoting individualized care and enhancing treatment outcomes.
By upholding patient rights, ensuring privacy and data protection, and respecting patient preferences during ESWT treatment, healthcare providers can foster a patient-centered care environment that prioritizes patient well-being and enhances the overall treatment experience.
Frequently Asked Questions

Get a Free Second Opinion
Experienced Burtom Medical Team is Ready to Help

I consent to Burtom Health Group using my aforesaid personal data for the purposes described in this notice and understand that I can withdraw my consent at any time by sending a request to info@burtom.com.