Burtom ‣ Technologies ‣ Digital Panoramic and Cephalometric Radiography
Language: 🇬🇧 English | 🇹🇷 Türkçe
Digital Panoramic and Cephalometric Radiography Overview

 Digital Panoramic and Cephalometric Radiography is a cutting-edge dental imaging technology that offers comprehensive views of the oral and maxillofacial regions. By capturing detailed panoramic images, it provides a broad perspective of the entire mouth, including the teeth, jaws, and surrounding structures. This panoramic view is invaluable for assessing overall dental health, identifying abnormalities, and planning various dental procedures such as orthodontic treatments, extractions, and implants.
Digital Panoramic and Cephalometric Radiography is a cutting-edge dental imaging technology that offers comprehensive views of the oral and maxillofacial regions. By capturing detailed panoramic images, it provides a broad perspective of the entire mouth, including the teeth, jaws, and surrounding structures. This panoramic view is invaluable for assessing overall dental health, identifying abnormalities, and planning various dental procedures such as orthodontic treatments, extractions, and implants.
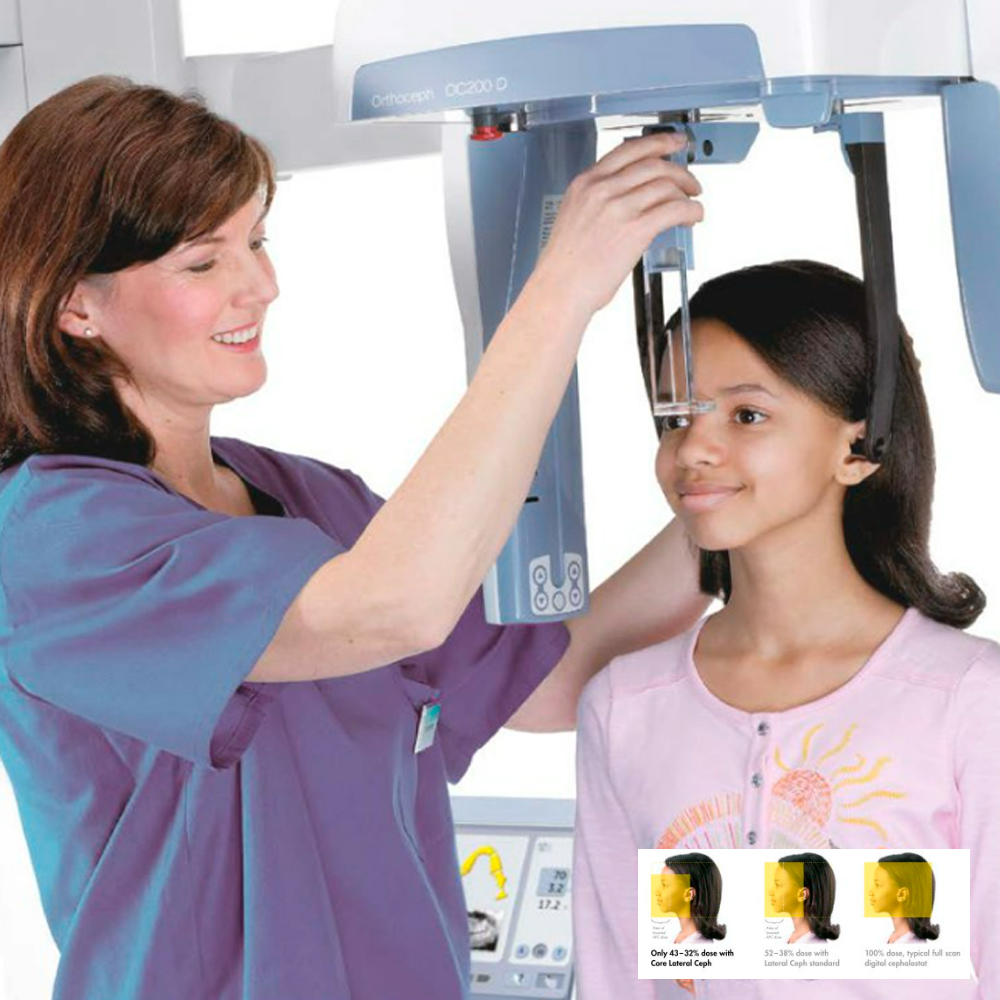
In addition to panoramic images, Cephalometric Radiography offers detailed lateral views of the skull, particularly focusing on the bones and soft tissues of the face and neck. This specialized imaging technique aids in diagnosing conditions related to facial symmetry, growth abnormalities, and airway obstructions. With precise measurements and analyses, Cephalometric Radiography plays a crucial role in orthodontic treatment planning, craniofacial surgery, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder evaluation.
One of the key advantages of Digital Panoramic and Cephalometric Radiography is its digital format, which allows for enhanced image quality, faster processing times, and easier storage and retrieval of patient data. Furthermore, the use of digital technology reduces radiation exposure compared to traditional film-based radiography, ensuring patient safety while still providing high-quality diagnostic images for comprehensive dental care.
What is Digital Panoramic and Cephalometric Radiography and How Does It Work?

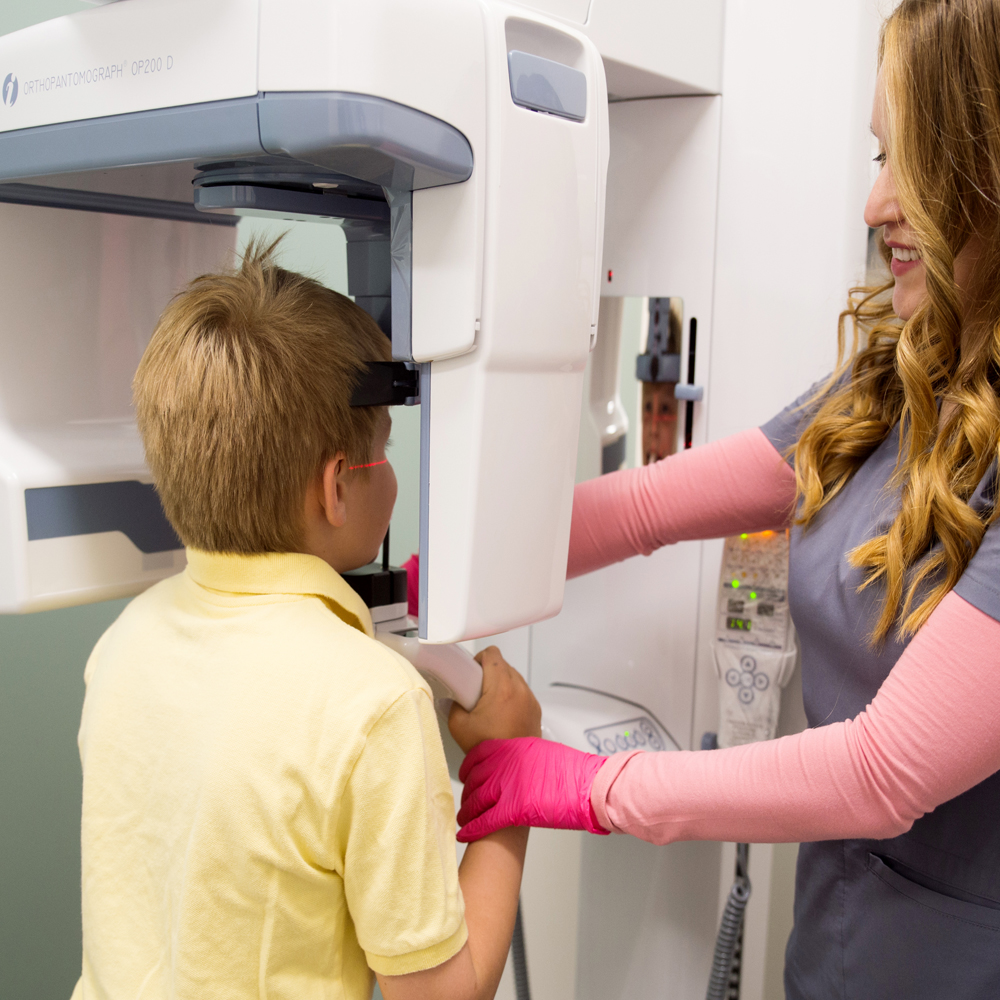
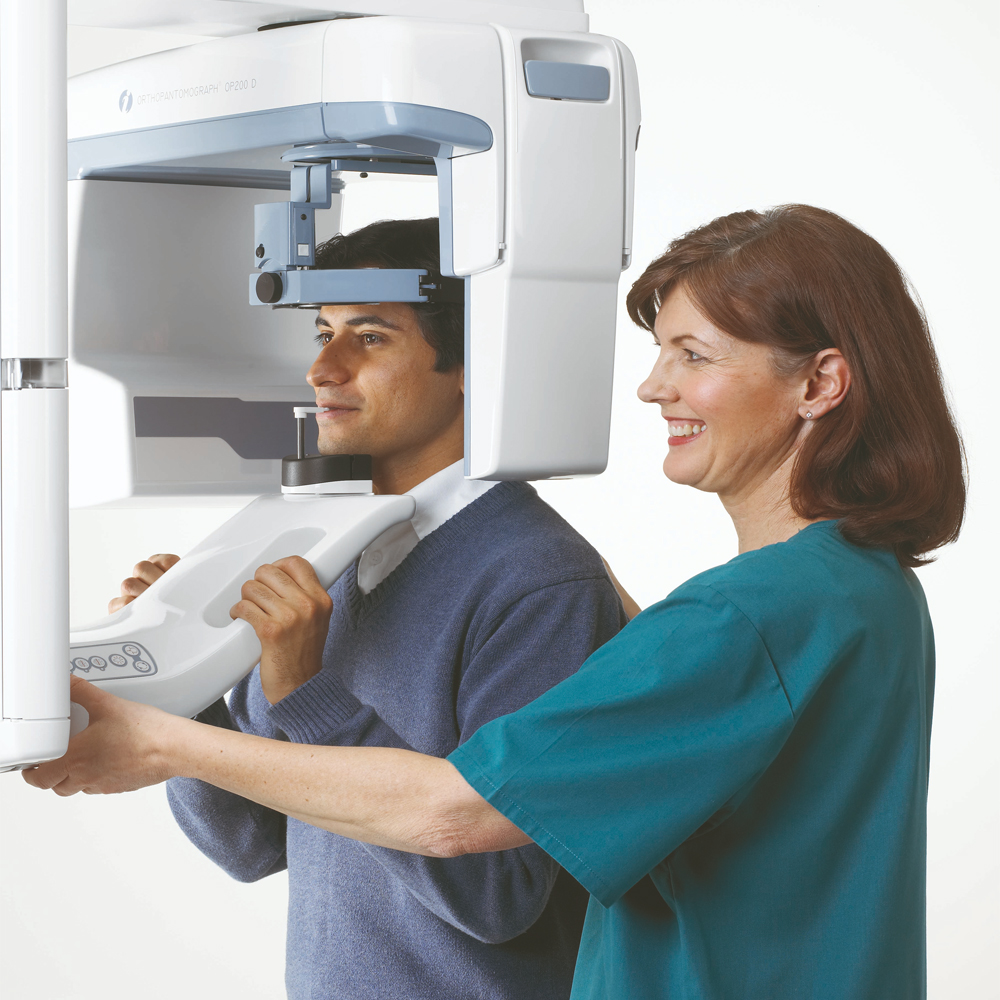
Digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography are advanced dental imaging techniques used to capture detailed images of the teeth, jaws, and surrounding structures. In digital panoramic radiography, a machine rotates around the patient’s head, capturing a single flat image of the entire mouth. Cephalometric radiography, on the other hand, involves taking side-view X-rays of the head to assess the relationship between the teeth, jaws, and facial bones. These digital imaging techniques utilize specialized sensors and software to produce high-resolution images, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment planning of various dental conditions.
The Basic Principle and Mechanism of Digital Panoramic and Cephalometric Radiography
The basic principle and mechanism of digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography involve the use of specialized X-ray machines to capture images of the entire dental and facial structures in a single exposure. In panoramic radiography, the X-ray source and receptor rotate around the patient’s head in opposite directions, creating a two-dimensional image that includes the teeth, jaws, and surrounding structures. Cephalometric radiography, on the other hand, captures lateral images of the head and neck, providing detailed views of the facial skeleton and soft tissues. Both techniques utilize digital sensors to convert X-ray signals into digital images, which can be manipulated and enhanced for diagnostic purposes.
How is the Digital Imaging of Dental and Facial Regions Achieved?
The digital imaging of dental and facial regions is achieved through the use of digital radiography systems specifically designed for dental applications. These systems utilize digital sensors, which are placed inside the patient’s mouth or positioned around the head and neck area, to capture X-ray images. When the X-ray beam penetrates the tissues and interacts with the sensor, it creates an electronic signal that is converted into a digital image. This image can then be viewed and manipulated on a computer screen, allowing for detailed examination and analysis of the dental and facial structures.
Applications and Importance of Digital Panoramic and Cephalometric Radiography
Digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography are widely used in dentistry for various diagnostic and treatment planning purposes.
Applications:
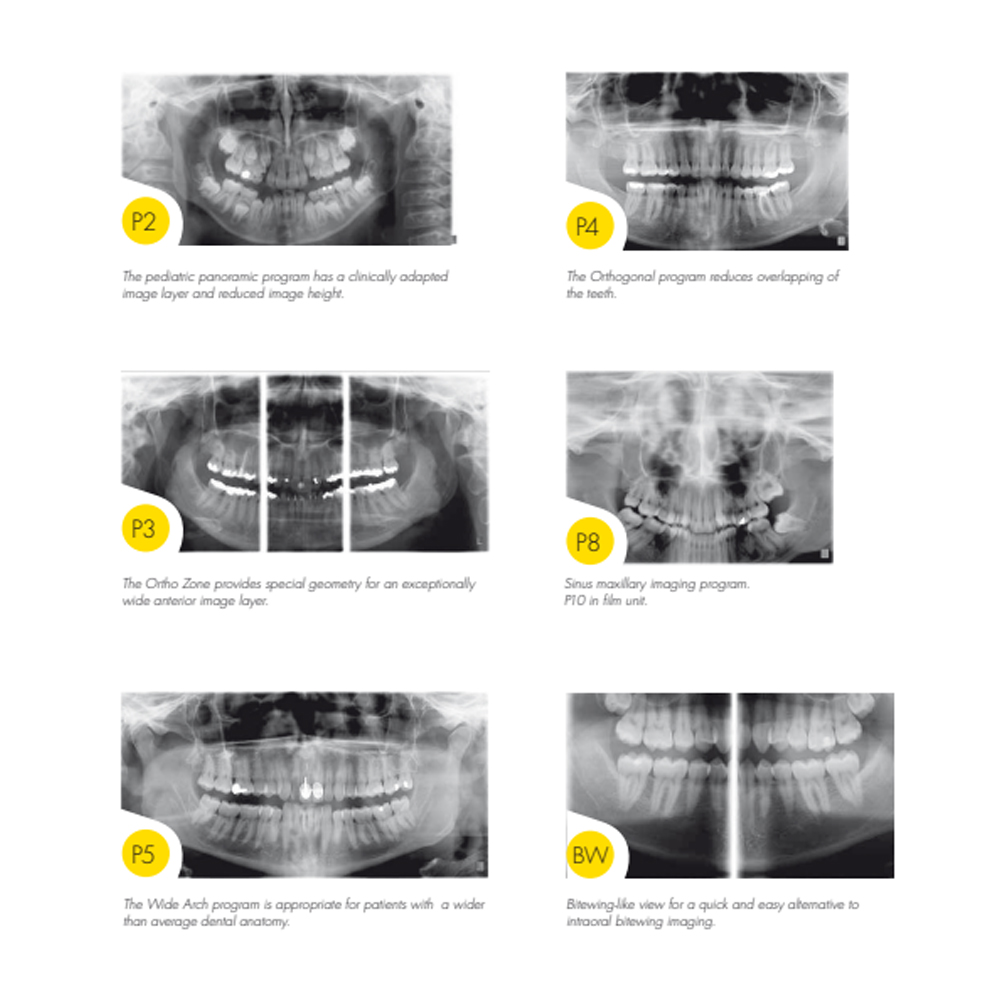
Diagnostic Imaging: Digital panoramic radiography provides a comprehensive overview of the entire dentition, jaws, and surrounding structures in a single image. It is valuable for detecting dental caries, periodontal diseases, impacted teeth, cysts, tumors, and other pathologies. Cephalometric radiography captures a lateral view of the head and aids in assessing craniofacial growth, orthodontic treatment planning, and identifying skeletal discrepancies.
Orthodontic Treatment Planning: Cephalometric radiographs are essential for orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning. They help orthodontists evaluate the relationship between the teeth and jaws, assess skeletal patterns, and determine the appropriate treatment approach, including the need for orthognathic surgery.
Implant Planning: Digital panoramic radiography is valuable for preoperative assessment in dental implant planning. It enables the evaluation of bone quality, quantity, and anatomy, facilitating the selection of suitable implant sites and the design of optimal implant placement strategies.
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Evaluation: Digital panoramic radiographs can provide useful information about the temporomandibular joint, including its position, morphology, and presence of any abnormalities or degenerative changes.
Periodontal Assessment: Digital panoramic radiographs aid in the assessment of periodontal conditions by visualizing bone levels, detecting bone loss, and evaluating the relationship between the teeth and surrounding alveolar bone.
Importance:
Comprehensive Visualization: Digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography offer a comprehensive view of the dentition, jaws, and surrounding structures, allowing for the detection of various dental and skeletal abnormalities in a single image.
Treatment Planning: These imaging modalities play a crucial role in treatment planning for various dental procedures, including orthodontic treatment, implant placement, TMJ evaluation, and periodontal therapy. They provide valuable diagnostic information that guides clinicians in developing effective treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs.
Diagnostic Accuracy: Digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography provide high-quality, detailed images with minimal radiation exposure compared to conventional film-based radiography. This enhances diagnostic accuracy and enables clinicians to make informed decisions regarding patient care.
Patient Comfort: Digital radiography systems offer faster image acquisition and reduced exposure time, improving patient comfort during the imaging process. Additionally, digital images can be easily stored, retrieved, and shared, facilitating efficient communication between dental professionals and interdisciplinary collaboration.
In summary, digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography are indispensable tools in modern dentistry, offering comprehensive visualization, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning, and prioritizing patient comfort and safety.
Contributions to the Evaluation of Dental and Jaw Anatomy: Digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography significantly contribute to the evaluation of dental and jaw anatomy by providing detailed images of the oral and maxillofacial structures. These imaging modalities offer a comprehensive view of the dentition, jaws, temporomandibular joints (TMJ), and surrounding tissues, enabling dentists and specialists to assess dental and skeletal abnormalities, bone morphology, and soft tissue structures. They play a crucial role in diagnosing conditions such as dental caries, periodontal disease, impacted teeth, developmental anomalies, TMJ disorders, and skeletal discrepancies.
Technology and Working Principle of Digital Panoramic and Cephalometric Radiography: Digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography utilize digital imaging technology to capture and process radiographic images of the oral and maxillofacial regions. In digital panoramic radiography, the patient’s head is positioned within the panoramic machine, and a rotating X-ray tube and detector assembly move around the patient’s head to capture a continuous image of the entire dental arches and surrounding structures. In cephalometric radiography, the patient’s head is positioned against a stationary image receptor, and a cone-shaped X-ray beam is directed through the patient’s head to produce a lateral view of the skull and facial bones.
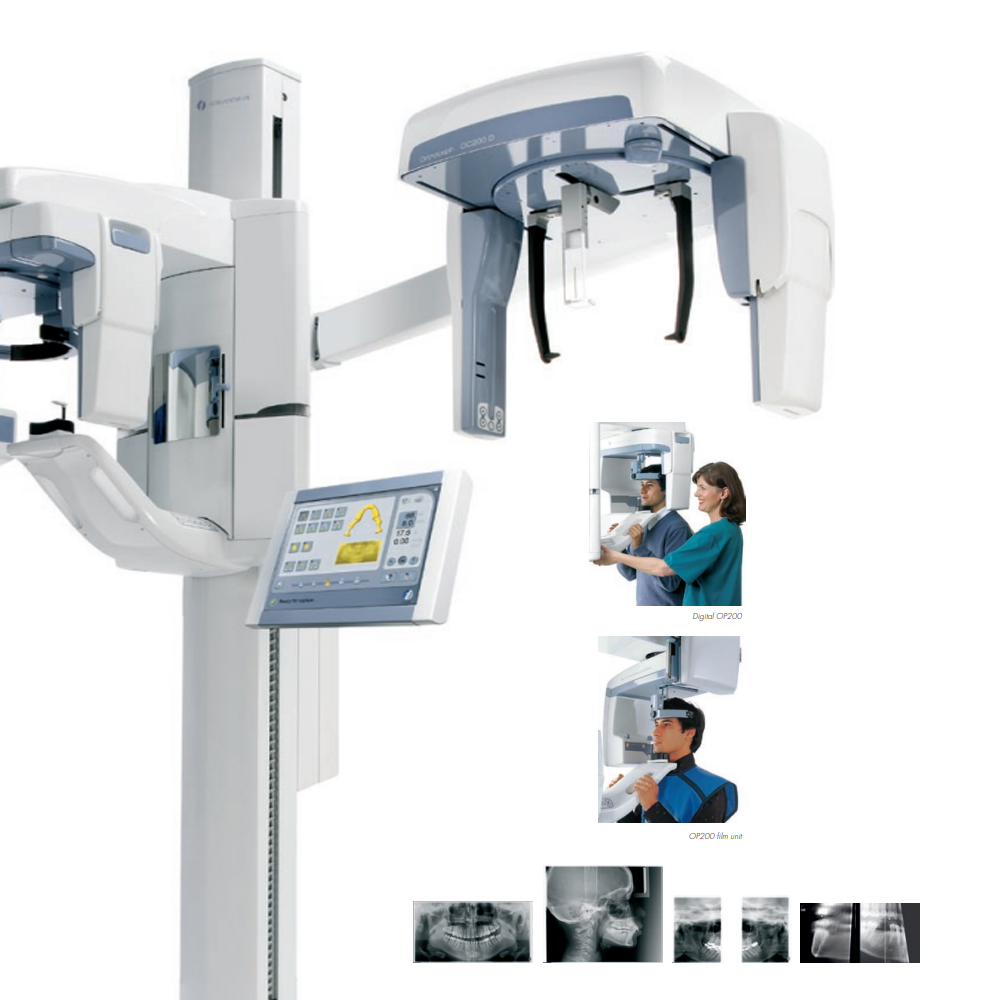
System Components of Digital Panoramic and Cephalometric Radiography: The components of digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography systems include:
X-ray Tube and Generator: The X-ray tube generates X-ray photons used to create the radiographic images. The X-ray generator controls the timing and intensity of the X-ray exposure.
Image Receptor: Digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography systems utilize digital image receptors, such as charged-coupled device (CCD) or complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) sensors, to capture the X-ray images.
Patient Positioning Devices: These devices ensure accurate positioning of the patient’s head during image acquisition to obtain optimal radiographic images.
Collimator: The collimator shapes and limits the X-ray beam to the desired area of interest, reducing unnecessary radiation exposure to the patient.
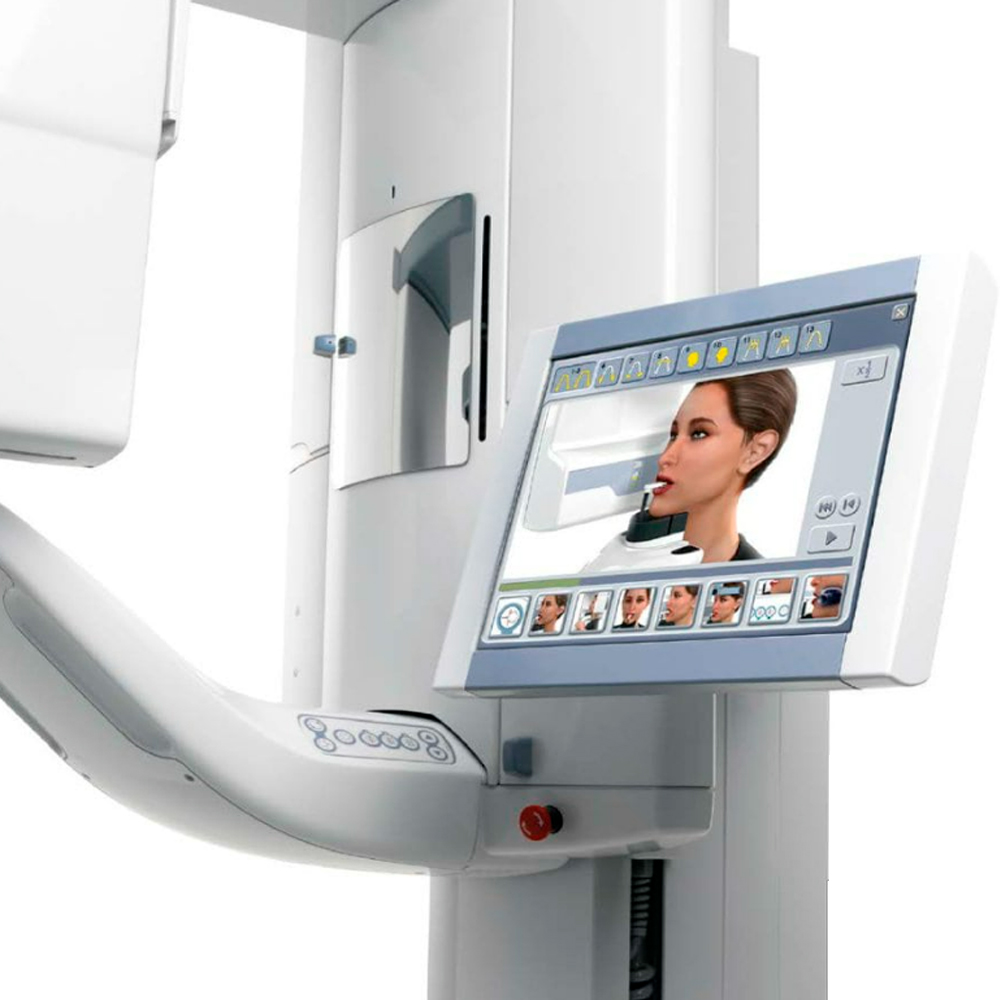
Image Processing Software: Digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography systems include software for image acquisition, processing, and display. This software enhances image quality, adjusts image parameters, and allows for measurements and annotations on the radiographic images.
Control Panel: The control panel enables the operator to adjust exposure settings, select imaging modes, and initiate image acquisition.
Display Monitor: The display monitor provides real-time visualization of the radiographic images for immediate evaluation and interpretation by the dental professional.
Overall, digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography systems consist of advanced components and technology designed to capture high-quality radiographic images of the oral and maxillofacial structures, contributing to accurate diagnosis and treatment planning in dentistry.
Image Acquisition and Processing: In digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography, image acquisition involves the use of X-ray technology to capture images of the oral and maxillofacial structures. These images are then processed using specialized software to enhance their quality and clarity. Digital processing allows for adjustments to be made to contrast, brightness, and sharpness, facilitating better visualization and interpretation by dental professionals.
Clinical Applications of Digital Panoramic and Cephalometric Radiography: Digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography find extensive applications in dentistry for diagnostic and treatment planning purposes. Panoramic radiographs provide a broad view of the entire dental arches, including teeth, jaws, and surrounding structures, making them valuable for identifying dental caries, periodontal disease, impacted teeth, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. Cephalometric radiographs, on the other hand, offer lateral views of the skull and facial bones, aiding in the assessment of skeletal relationships, orthodontic treatment planning, and surgical interventions.
Evaluation of Dental and Jaw Structure and Diagnosis of Diseases: Digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography play a pivotal role in evaluating dental and jaw structures and diagnosing various dental and maxillofacial diseases. Panoramic radiographs enable dentists to assess the presence of dental anomalies, such as missing teeth, supernumerary teeth, and dental fractures, as well as identify abnormalities in the jawbones, such as cysts, tumors, and developmental defects. Cephalometric radiographs provide detailed views of the craniofacial skeleton, facilitating the diagnosis of skeletal discrepancies, facial asymmetry, and orthodontic irregularities. Additionally, these imaging modalities aid in the early detection of dental and maxillofacial pathologies, allowing for timely intervention and treatment planning.
Advantages and Benefits of Digital Panoramic and Cephalometric Radiography:
High Resolution and Detailed Imaging: Digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography provide high-resolution images with detailed anatomical information of the dental and maxillofacial structures. This allows for accurate assessment and diagnosis of dental and skeletal abnormalities.
Ease and Accuracy for Patients and Dentists: These imaging modalities offer convenience and efficiency for both patients and dental professionals. Patients experience minimal discomfort during image acquisition, as the process is non-invasive and requires minimal patient cooperation. Dentists benefit from the ease of image acquisition and interpretation, leading to precise diagnosis and treatment planning.
Comprehensive Views of Dental and Maxillofacial Structures: Digital panoramic radiography offers a comprehensive view of the entire dental arches, including teeth, jaws, and surrounding structures, in a single image. Similarly, cephalometric radiography provides lateral views of the skull and facial bones, enabling dentists to assess skeletal relationships and orthodontic irregularities accurately.
Time-Efficient Imaging Process: Digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography involve quick image acquisition and processing, leading to time-efficient diagnostic workflows in dental practices. This allows for prompt diagnosis and treatment planning, contributing to enhanced patient care and satisfaction.
Digital Data Storage and Retrieval: Digital imaging technology allows for the storage and retrieval of radiographic images in electronic formats. This facilitates seamless integration with electronic health records (EHRs) and enables easy access to patient data for dental professionals. Additionally, digital images can be easily shared with specialists and referring practitioners, promoting interdisciplinary collaboration in patient care.
Reduced Radiation Exposure: Compared to traditional film-based radiography, digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography involve lower radiation doses, ensuring patient safety while maintaining diagnostic image quality. This reduction in radiation exposure aligns with the principle of ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) in radiological imaging.
Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities: Digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities through advanced image processing techniques. Dentists can manipulate image parameters such as contrast, brightness, and magnification to optimize image quality and visualize specific anatomical structures better, leading to more accurate diagnoses.
Overall, digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography provide numerous advantages and benefits, including high-resolution imaging, ease of use, comprehensive views of dental and maxillofacial structures, time efficiency, digital data storage, reduced radiation exposure, and enhanced diagnostic capabilities, contributing to improved patient care and clinical outcomes in dentistry.
Safety of Digital Panoramic and Cephalometric Radiography Scanning:
Radiation Exposure and Safety Measures: Digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography utilize X-ray technology to produce images of the dental and maxillofacial structures. While the radiation dose associated with these imaging modalities is relatively low compared to other radiographic techniques, it is essential to implement safety measures to minimize patient exposure.
Precautions Taken for Patient Safety During Scanning: Dental professionals adhere to strict protocols to ensure patient safety during panoramic and cephalometric radiography scanning. These precautions include:
Lead Aprons and Thyroid Collars: Patients wear lead aprons to shield the body from unnecessary radiation exposure, while thyroid collars protect the thyroid gland during cephalometric imaging.
Positioning and Immobilization: Proper positioning of the patient’s head and neck is crucial to minimize movement during image acquisition, thereby reducing the likelihood of image artifacts and the need for repeat exposures.
Adjusting Exposure Parameters: Dental radiographers adjust exposure parameters such as exposure time and radiation intensity based on the patient’s size, age, and diagnostic requirements to optimize image quality while minimizing radiation dose.
ALARA Principle: Adherence to the ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) principle ensures that radiation exposure is kept to the minimum necessary for diagnostic purposes without compromising image quality.
Radiation Exposure Monitoring and Regulation: Dental facilities employ radiation monitoring devices and adhere to regulatory guidelines to ensure compliance with safety standards. Regular calibration and maintenance of radiographic equipment are essential to maintain optimal performance and minimize radiation exposure.
Patient Education and Informed Consent: Patients receive comprehensive information about the benefits and risks of panoramic and cephalometric radiography, including radiation exposure, during the informed consent process. This allows patients to make informed decisions regarding their dental care while understanding the safety measures in place to protect their health.
Continuous Professional Training: Dental professionals undergo continuous training and education on radiation safety protocols and best practices for panoramic and cephalometric radiography. This ensures that they remain updated on the latest safety guidelines and techniques to minimize radiation exposure while obtaining diagnostic images of high quality.
Overall, the safety of digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography scanning is ensured through the implementation of stringent safety measures, adherence to regulatory guidelines, patient education, and continuous professional training, thereby minimizing radiation exposure while maintaining diagnostic efficacy in dental imaging.
Improvements in Imaging Techniques and Future Potential:
Continual advancements in imaging technology have led to significant improvements in digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography, enhancing diagnostic capabilities and patient care. These advancements include:
Enhanced Image Quality: Ongoing developments in digital sensor technology and image processing algorithms have resulted in higher resolution and improved image quality, allowing for more accurate diagnosis of dental and craniofacial conditions.
Three-Dimensional Imaging: Integration of three-dimensional (3D) imaging capabilities into panoramic and cephalometric radiography systems enables dental practitioners to visualize dental and craniofacial structures in three dimensions, providing valuable information for treatment planning and evaluation.
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Integration: Integration of CBCT functionality into panoramic and cephalometric radiography systems expands imaging capabilities, allowing for comprehensive assessment of dental and craniofacial anatomy with increased detail and accuracy.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Applications: The integration of AI algorithms into digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography systems holds promise for enhancing diagnostic accuracy, automating image analysis tasks, and improving workflow efficiency in dental practice.
Portable and Point-of-Care Imaging: Advancements in portable panoramic and cephalometric radiography devices facilitate point-of-care imaging, enabling dental practitioners to obtain diagnostic images conveniently at the patient’s bedside or in remote settings.
Patient Rights and Important Considerations Regarding Digital Panoramic and Cephalometric Radiography:
Patient rights and considerations play a crucial role in ensuring ethical and safe dental imaging practices. Some key aspects to consider regarding digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography include:
Informed Consent: Patients have the right to receive comprehensive information about the purpose, benefits, risks, and alternatives of digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography. Obtaining informed consent from patients demonstrates respect for their autonomy and allows them to make informed decisions about their dental care.
Radiation Safety: Ensuring patient safety is paramount when performing digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography. Dental practitioners should adhere to radiation safety protocols, such as minimizing radiation exposure by using appropriate shielding and optimizing imaging parameters based on patient characteristics.
Privacy and Confidentiality: Dental practitioners must uphold patient privacy and confidentiality by securely storing and handling digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography images in compliance with healthcare data protection regulations. Patients have the right to expect their personal health information to be safeguarded from unauthorized access or disclosure.
Patient Comfort and Well-being: Dental practitioners should prioritize patient comfort and well-being during digital panoramic and cephalometric radiography procedures. Measures such as providing clear instructions, addressing patient concerns, and ensuring proper positioning can enhance the patient experience and minimize discomfort during imaging.
Frequently Asked Questions

Get a Free Second Opinion

I consent to Burtom Health Group using my aforesaid personal data for the purposes described in this notice and understand that I can withdraw my consent at any time by sending a request to info@burtom.com.