Burtom ‣ Technologies ‣ Electromyography (EMG/ENMG)
Language: 🇬🇧 English | 🇹🇷 Türkçe
Electromyography (EMG/ENMG) Overview

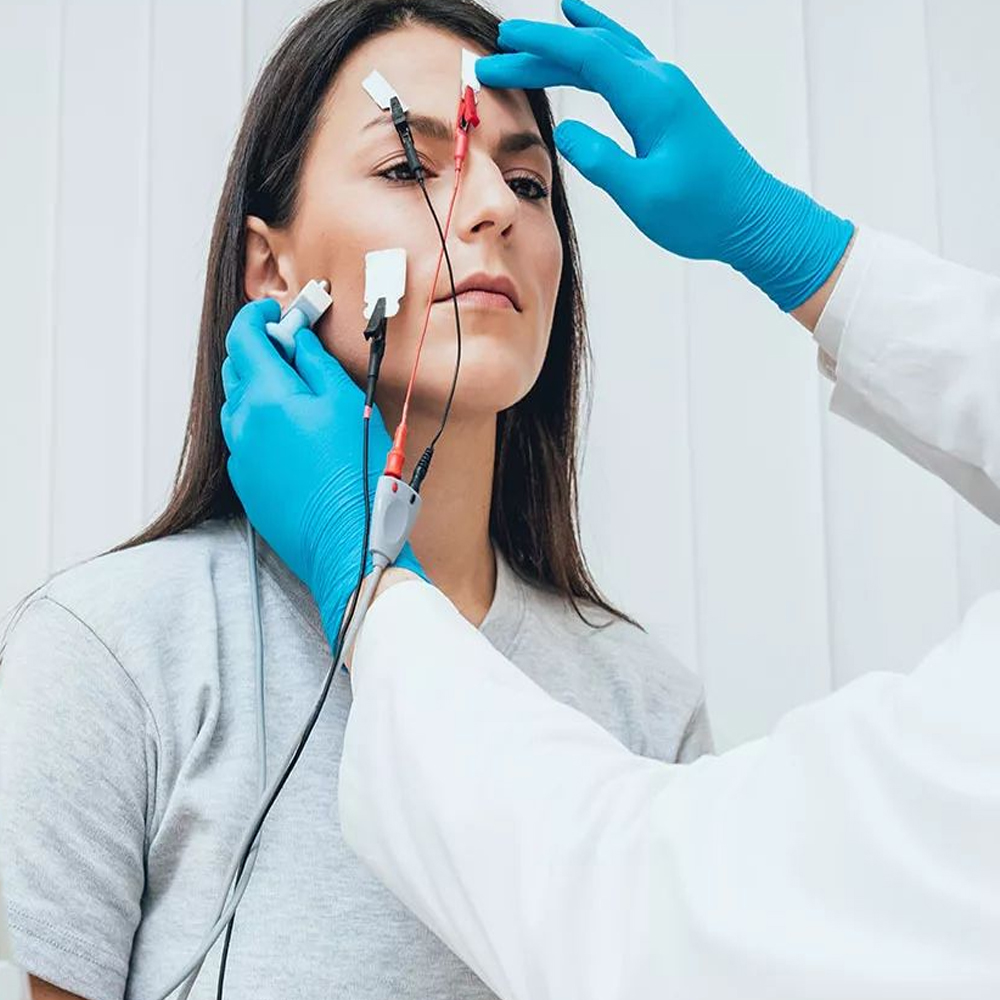
 Electromyography (EMG), also known as electroneuromyography (ENMG), is a diagnostic procedure used to assess the electrical activity of muscles and the associated nerves. It is commonly employed to diagnose and evaluate disorders affecting the neuromuscular system, including nerve compression or injury, muscle disorders, and disorders of the nerve roots.
Electromyography (EMG), also known as electroneuromyography (ENMG), is a diagnostic procedure used to assess the electrical activity of muscles and the associated nerves. It is commonly employed to diagnose and evaluate disorders affecting the neuromuscular system, including nerve compression or injury, muscle disorders, and disorders of the nerve roots.
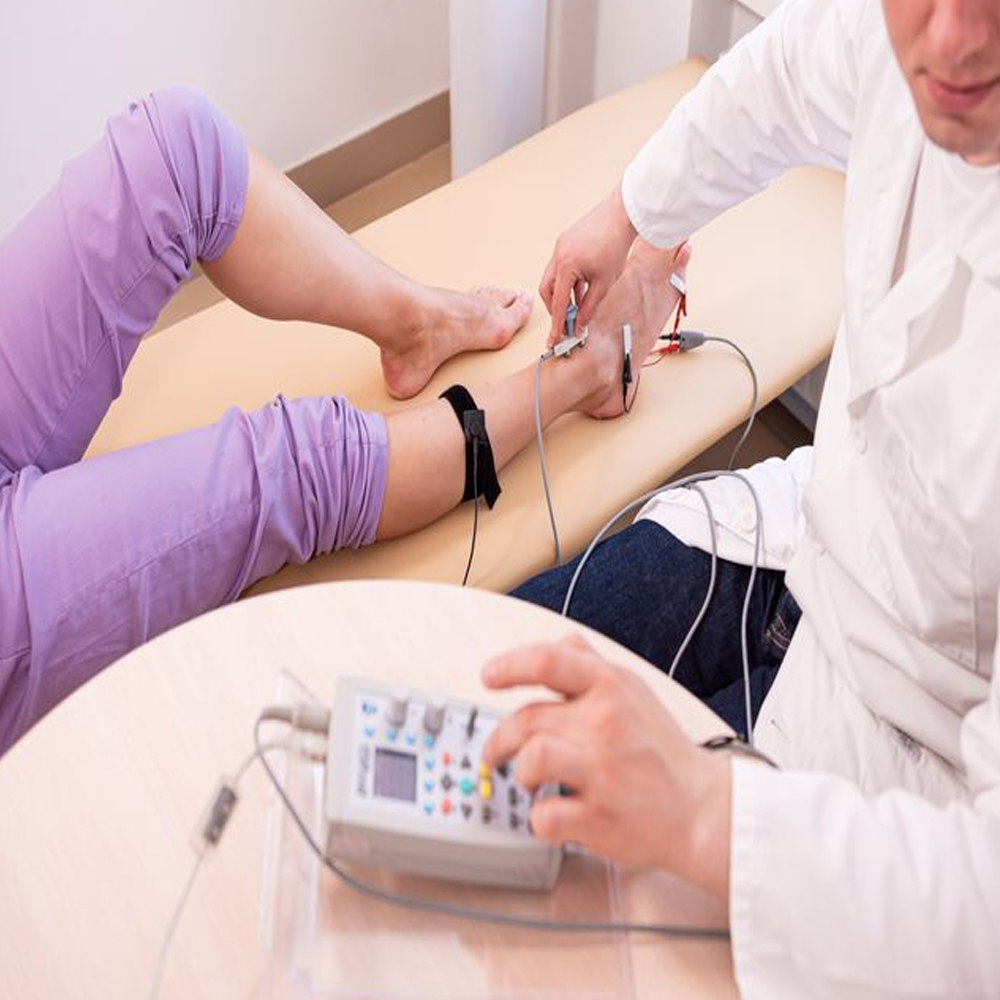
During an EMG procedure, small electrodes are inserted into the muscles being studied, and the electrical activity of these muscles is recorded while the patient performs various voluntary movements or when the muscles are at rest. The resulting electrical signals, called electromyograms, provide valuable information about the health and function of the muscles and nerves.
EMG is often used in conjunction with nerve conduction studies (NCS), another diagnostic test that assesses the function of peripheral nerves. Together, EMG and NCS help clinicians identify the location and extent of nerve or muscle damage, determine the cause of symptoms such as weakness, pain, or numbness, and formulate appropriate treatment plans.
This diagnostic tool is commonly used in the evaluation of conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome, peripheral neuropathies, radiculopathies, myopathies, motor neuron diseases, and other neuromuscular disorders. EMG findings can provide valuable insights into the underlying pathology and help guide treatment decisions, rehabilitation strategies, and monitoring of disease progression.
What Is Electromyography (EMG/ENMG) and How Does It Work?

Electromyography (EMG/ENMG) is a diagnostic technique used to evaluate the electrical activity produced by muscles and the nerves controlling them. It involves placing electrodes on the skin or directly into muscles to measure and record electrical signals, known as electromyograms. These signals provide valuable information about muscle function, nerve health, and the presence of any abnormalities or disorders affecting the neuromuscular system. By analyzing these signals, healthcare professionals can assess muscle and nerve function, diagnose neuromuscular conditions, and develop treatment plans tailored to the patient’s needs.
The Basic Principle and Purpose of Electromyography: Electromyography (EMG/ENMG) operates on the principle of detecting and analyzing the electrical signals generated by muscles and the nerves controlling them. Its primary purpose is to assess the health and function of the neuromuscular system by measuring the electrical activity produced during muscle contractions and at rest.
Measurement and Analysis of Nerve and Muscle Signals: In EMG/ENMG, electrodes are placed on the skin surface or inserted directly into muscles to capture the electrical signals. These signals, called electromyograms, are then recorded and analyzed to evaluate the integrity of nerve-muscle communication, identify abnormalities or disorders affecting the neuromuscular system, and guide diagnosis and treatment decisions. Through precise measurement and analysis of these signals, healthcare professionals gain insights into muscle function, nerve health, and the presence of any neuromuscular conditions.
Technology and Operating Principle of Electromyography: Electromyography (EMG/ENMG) utilizes advanced technology to assess the electrical activity of muscles and nerves. The operating principle involves detecting and recording these electrical signals generated during muscle contractions and at rest. By analyzing the characteristics of these signals, EMG/ENMG provides valuable insights into neuromuscular function and helps diagnose a wide range of disorders affecting the neuromuscular system.
Basic Components and Operation of EMG/ENMG Device: The EMG/ENMG device consists of essential components such as electrodes, amplifiers, and signal processing units. Electrodes are placed on the skin surface or inserted into muscles to capture electrical signals, which are then amplified and processed by the device. The operation involves acquiring, amplifying, filtering, and analyzing the electromyographic signals to assess muscle and nerve function accurately.
Assessment of Neuromuscular Disorders: EMG/ENMG plays a crucial role in assessing and diagnosing various neuromuscular disorders, including nerve injuries, muscle diseases, and motor neuron disorders. By evaluating the electrical activity of muscles and nerves, EMG/ENMG helps healthcare professionals identify abnormalities, determine the extent of nerve damage, and differentiate between different types of neuromuscular conditions. This diagnostic tool aids in developing targeted treatment plans and monitoring the progress of neuromuscular disorders over time.
Detection of Nerve Damage and Muscle Weakness: Electromyography (EMG/ENMG) plays a crucial role in detecting nerve damage and muscle weakness by analyzing the electrical activity of muscles and nerves. This diagnostic tool helps identify abnormalities in neuromuscular function, allowing for early intervention in conditions such as peripheral neuropathies and radiculopathies.
Diagnosis and Rehabilitation of Muscle Diseases: EMG/ENMG is instrumental in diagnosing and rehabilitating muscle diseases by assessing the severity and extent of muscle involvement. It provides valuable information for designing personalized rehabilitation programs and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment interventions aimed at improving muscle function and strength in conditions such as myopathies and muscular dystrophies.
Advantages and Benefits of Electromyography: EMG/ENMG offers several advantages and benefits in clinical practice. It provides objective and quantitative measurements of muscle and nerve function, allowing for accurate diagnosis and treatment monitoring. Additionally, it is non-invasive and well-tolerated by patients, making it a valuable tool for assessing neuromuscular disorders across various age groups and patient populations.
Clinical Applications of Electromyography: EMG/ENMG has diverse clinical applications, including but not limited to diagnosing nerve damage, assessing muscle function, monitoring disease progression, guiding treatment decisions, and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions. Its versatility and accuracy make it an indispensable tool in neurology, orthopedics, rehabilitation medicine, and sports medicine.
Diagnostic Sensitivity and Specificity: Electromyography (EMG/ENMG) exhibits high diagnostic sensitivity and specificity in detecting abnormalities in neuromuscular function. By accurately measuring and analyzing the electrical activity of muscles and nerves, EMG/ENMG helps differentiate between various neuromuscular disorders, contributing to precise diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
Contribution to Treatment and Rehabilitation Planning: EMG/ENMG plays a significant role in treatment and rehabilitation planning by providing valuable information about the extent and severity of neuromuscular impairments. It aids healthcare professionals in developing tailored treatment strategies, including physical therapy, medication, or surgical interventions, to address specific muscle and nerve dysfunctions identified through EMG/ENMG testing.
Risks and Side Effects of Electromyography: While EMG/ENMG is generally considered safe, it may involve certain risks and side effects. Common side effects include temporary discomfort or pain at the electrode insertion sites and minor bruising or bleeding. In rare cases, patients may experience allergic reactions to electrode materials or infection at the insertion sites. However, these risks are minimal and can be mitigated by following proper sterile techniques during the procedure.
Potential Complications and Precautions: Although uncommon, potential complications of EMG/ENMG may include nerve injury, muscle damage, or excessive bleeding at the electrode insertion sites. Healthcare providers should exercise caution when performing EMG/ENMG procedures, especially in patients with pre-existing neurological conditions or bleeding disorders. Precautionary measures, such as proper patient positioning, careful electrode placement, and monitoring for signs of adverse reactions during and after the procedure, can help minimize the risk of complications.
Considerations During Electromyography: During electromyography (EMG/ENMG) testing, several considerations should be taken into account to ensure optimal outcomes and patient comfort. These include explaining the procedure thoroughly to the patient, addressing any concerns or questions they may have, ensuring a calm and comfortable environment, and minimizing any potential discomfort during electrode placement and muscle stimulation. Additionally, healthcare providers should be attentive to patient positioning and communication throughout the testing process to facilitate accurate readings and improve overall patient experience.
Patient Experience and Comfort During Electromyography Use: Patient experience and comfort are essential aspects of electromyography (EMG/ENMG) testing. Healthcare providers should strive to create a supportive and reassuring atmosphere, addressing any anxieties or apprehensions the patient may have regarding the procedure. This can involve providing clear instructions, maintaining open communication, and offering emotional support throughout the testing process. Additionally, efforts should be made to minimize discomfort during electrode placement and muscle stimulation, ensuring a positive and comfortable experience for the patient.
Patient Impressions and Comfort During Testing: Patient impressions and comfort during electromyography (EMG/ENMG) testing play a crucial role in overall satisfaction and compliance with the procedure. Healthcare providers should prioritize patient-centered care, taking into account individual preferences and concerns to enhance the testing experience. This includes explaining the purpose and steps of the procedure, addressing any discomfort or pain promptly, and actively involving the patient in decision-making processes. By fostering a collaborative and supportive environment, healthcare providers can improve patient comfort and satisfaction during EMG/ENMG testing.
Post-Test Recovery and Patient Satisfaction: After electromyography (EMG/ENMG) testing, patients may experience minor discomfort or fatigue at the electrode insertion sites. Healthcare providers should provide post-test instructions and recommendations to promote recovery and alleviate any lingering discomfort. This may include advising patients to avoid strenuous activities for a short period, applying ice or heat packs to reduce soreness, and taking over-the-counter pain medication as needed. Additionally, healthcare providers should follow up with patients to address any concerns or questions they may have post-test, ensuring overall satisfaction and continuity of care.
Improvement and Interpretation of Test Results: Efforts to enhance electromyography (EMG/ENMG) testing include ongoing advancements in technology and methodologies aimed at improving the accuracy and reliability of test results. This involves refining electrode placement techniques, optimizing signal acquisition parameters, and developing sophisticated analysis algorithms to interpret data more effectively. Additionally, interdisciplinary collaboration between healthcare professionals, engineers, and researchers contributes to the continual improvement of EMG/ENMG testing methods, ensuring more precise diagnosis and treatment planning for patients.
Patient Rights and Considerations Regarding Electromyography: Respecting patient rights and considerations during electromyography (EMG/ENMG) testing is paramount to uphold ethical standards and promote patient-centered care. Patients have the right to be informed about the purpose, risks, and potential benefits of the procedure, as well as to provide informed consent before testing. Additionally, healthcare providers should prioritize patient privacy, confidentiality, and autonomy throughout the testing process, ensuring that patients feel respected, empowered, and involved in their healthcare decisions.
Privacy and Data Protection: Maintaining patient privacy and data protection is crucial in electromyography (EMG/ENMG) testing to safeguard sensitive medical information and uphold patient confidentiality. Healthcare providers must adhere to strict privacy regulations and security protocols when collecting, storing, and transmitting patient data obtained during testing. This includes implementing encryption measures, access controls, and secure data storage systems to prevent unauthorized access or breaches of patient information, thereby ensuring compliance with healthcare privacy laws and regulations.
Patient Rights and Preferences During Testing: Recognizing and respecting patient rights and preferences during electromyography (EMG/ENMG) testing is essential for promoting patient satisfaction and engagement in their healthcare experience. Healthcare providers should prioritize open communication, active listening, and shared decision-making, allowing patients to express their preferences regarding test procedures, comfort measures, and post-test care. By acknowledging and accommodating individual patient needs and preferences, healthcare providers can enhance the overall testing experience and foster a collaborative patient-provider relationship.
Advancements and Improvement Potential in Diagnosis and Treatment Processes: Ongoing advancements in electromyography (EMG/ENMG) technology and methodologies hold significant potential for improving the diagnosis and treatment of neuromuscular disorders. Emerging technologies, such as high-density surface electromyography and advanced signal processing techniques, enable more detailed assessment of muscle activity and neuromuscular function, leading to more accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment interventions. Additionally, interdisciplinary research collaborations and technological innovations continue to drive progress in diagnostic algorithms, treatment protocols, and therapeutic modalities, offering promising opportunities to enhance patient outcomes and quality of care.
Frequently Asked Questions

Get a Free Second Opinion

I consent to Burtom Health Group using my aforesaid personal data for the purposes described in this notice and understand that I can withdraw my consent at any time by sending a request to info@burtom.com.